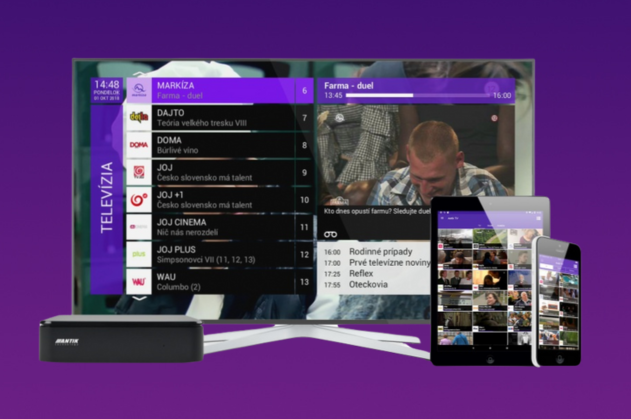
Is a heat pump worth it?
When to use it and when not to?
A heat pump is an economical source of heating, but it has its own specifics. It works optimally at low water temperatures of up to 35°C, so it is optimal to use it with low-temperature underfloor heating. Of course, a combination with radiators is also possible, they should ideally be low-temperature with a large surface area. When using older radiators with a need for higher water temperatures, the heat pump will also work, but its efficiency will be lower.
The performance of the heat pump will be verified by calculation in the thermal assessment of your home after the inspection. In the case of switching from another type of heating, we will also suggest the most ideal way to rebuild the current heating while keeping the appropriate components and also a combination of multiple heating sources, as our heat pump can choose the cheapest heating source at a given time according to current energy prices. The control will therefore be a combination of equithermal curves and smart control.
If you choose a combination of a heat pump with photovoltaics, we will set up the system to maximize the use of photovoltaics while maintaining the thermal comfort of your home. You will have the heat pump, photovoltaics, electric car charging and household consumption constantly under control in one application with the possibility of connecting to other smart home elements.
First offer
In the first non-binding offer, we will recommend the type and performance of the heat pump according to the basic parameters you have entered:

We will also estimate the costs of its operation compared to other energy sources, so that you have a rough idea of how much you will improve compared to your current heating source and what the return on investment is:

Where can you use a heat pump?
- new buildings - well-insulated houses with underfloor heating, an ideal solution
- home renovations with a gas boiler - replacing gas heating with a heat pump is ideal if your gas boiler has reached the end of its service life and you are considering what to do next. A heat pump is a good choice, but you need to choose the right type and assess the condition of the heating system. Compared to gas, a heat pump has one huge advantage: you can produce electricity yourself at home using photovoltaics!
- Renovations of houses with an electric boiler - here, replacing it with a heat pump is clearly recommended, as a heat pump will immediately save you 70% of your electricity costs.
- houses with solid fuel heating - are you tired of finding and handling wood every year? Switch to a heat pump and heat your fireplace only when you really feel like it.
What is the return?
The return depends on several factors:
-
Heating system - underfloor heating, radiators or a combination, each solution requires a different water temperature and thus changes the heating efficiency
-
Previous heating method - if you were heating with wood, the payback in money will be very long, in this case you will save mainly on labor. If you are switching from an electric boiler, the payback can be as little as 3 years. In the case of switching from a gas boiler, it depends on the current price of gas and ranges between 6 and 10 years.
- What subsidy will you receive - subsidy shortens the return
COP and SCOP
These two abbreviations can be seen on every heat pump, but what do they mean? COP is the "coefficient of performance" and is a figure that tells you how many kW of heat the pump currently produces per 1 kW of energy consumed. COP=4.7 means that for 1 kW of electrical energy consumption, the pump produces 4.7 kW of heat.
The COP parameter is strongly dependent on the temperature of the outside air and the temperature of the water it heats. The colder it is outside, the lower the COP and the higher the temperature of the water in the heating system, the lower the COP. These parameters are constantly changing throughout the year, which means that the current COP is always different. That is why there is the SCOP parameter "seasonal coefficient of performance", i.e. the annual average COP and objectively speaks about the efficiency of the heat pump in given climatic conditions throughout the year.
In our conditions, SCOP will be around 3.5 for low-temperature heating and around 2.5 for high-temperature heating.