Optimizers
What is an optimizer?
Panels in a photovoltaic system are connected in series strings, and a feature of this connection is that the entire string works as well as the weakest panel in the string. So if one panel is shaded, all panels in the string behave as if they were shaded.
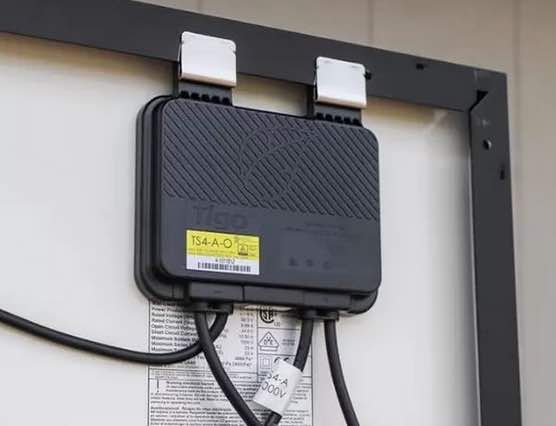
An optimizer is a small electronic device that is usually mounted on the bottom of a solar panel or a group of panels. Its main purpose is to maximize the output of each panel, especially in cases where there is partial shading or other influences that could limit energy production.

One of the main advantages of optimizers is that they allow each solar panel to operate independently of the others. This means that if one panel is partially shaded (e.g. by a tree, chimney or other obstacle), it will not affect the performance of the other panels.

How do optimizers work?
The optimizer works on the principle of the so-called Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). Every solar panel has an optimal point at which it is capable of producing the most energy at any given time, and this point changes depending on lighting conditions, temperature, and other factors. The optimizer ensures that each panel operates at its maximum output, independently of the other panels in the system.
When is it worth using an optimizer?
Partial shading: One of the most common reasons for using optimizers is when solar panels are not exposed to direct sunlight all day. If your roof or property is surrounded by trees, buildings, or other obstacles that create shadows, an optimizer can help maximize energy production, even in conditions where performance would be significantly lower without an optimizer.
Complicated roof shape: If your roof has an irregular shape, different slopes, or is divided into several parts where the solar panels are located in different places and oriented to different cardinal points, an optimizer can help significantly. It will allow each panel to work at its maximum without being limited by the performance of the other panels.
Panel level monitoring: Modern systems with optimizers often allow detailed monitoring of the performance of each individual panel. If you care about maximum visibility into how your system is performing and want to be able to quickly detect potential problems (e.g. a faulty panel or shading), optimizers offer this level of control and insight.
When is an optimizer not worth it?
Good conditions: as long as your solar panels are installed on a flat, sunny surface that is not affected by shade. In such ideal conditions, the panels will be able to work efficiently without further optimization, and we believe that investing in optimizers is unnecessary.
Additional costs: Installing optimizers increases the overall cost of the photovoltaic system and worsens the return on investment. Therefore, at Antik, we try to design the layout of the panels so that their use is not necessary and we recommend them only where it is really necessary.